What is High Bandwidth Memory, and Why is the US Blocking China’s Access?
The United States government has tightened export controls, aiming to restrict China’s access to high bandwidth memory (HBM) technology. These cutting-edge semiconductors are crucial for artificial intelligence (AI) applications, and the restrictions could have significant implications for global technology and geopolitical dynamics.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of what HBM is, why it matters, and how these restrictions could impact China.
What is High Bandwidth Memory (HBM)?
HBM is an advanced type of memory chip designed to store and transmit data at unprecedented speeds. Unlike traditional DRAM (Dynamic Random Access Memory), HBM stacks memory chips vertically, enabling greater data storage and faster performance.
These chips are vital for:
- AI Applications: Powering AI processors, such as GPUs made by Nvidia and AMD.
- High-Performance Computing: Used in data centers and autonomous vehicles.
- Graphic Cards: Supporting complex gaming and rendering tasks.
“HBM is like the memory of a brain—it’s indispensable for AI,” explains G. Dan Hutcheson, Vice Chair of TechInsights. Without HBM, AI processors would lack the ability to store and access the vast amounts of data they require.
Graphic: Rosa de Acosta, CNN
Why is HBM Critical for AI?
HBM stands out due to its larger storage capacity and faster data transmission speeds. This makes AI applications run more efficiently, reducing delays and improving performance.
To illustrate, Hutcheson compares HBM’s higher bandwidth to a highway:
“Think of a two-lane road versus a hundred-lane highway. With HBM, data flows seamlessly without bottlenecks, enabling AI systems to handle complex computations.”
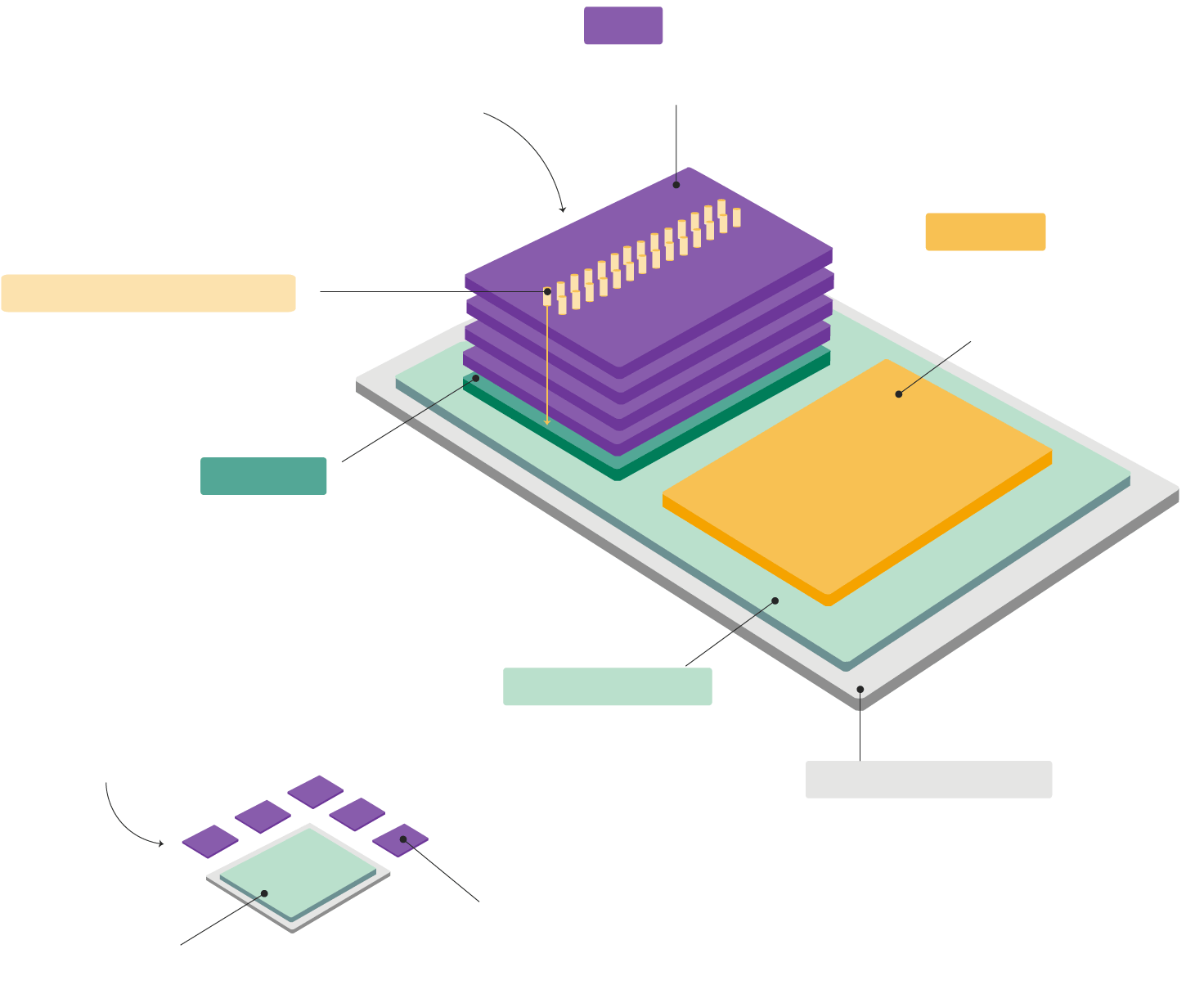
How is HBM Made?
HBM manufacturing involves a sophisticated process of stacking memory chips like layers of a hamburger. However, creating these chips requires extreme precision:
- Thin Layers: Each chip layer is as thin as half a strand of hair.
- Advanced Packaging: Holes must be drilled with pinpoint accuracy for electric wires, akin to constructing a delicate house of cards.
These challenges contribute to HBM’s high cost—several times that of conventional memory chips.
Who Dominates the HBM Market?
Three companies lead the global HBM market:
- SK Hynix (South Korea) – 50% market share in 2022.
- Samsung (South Korea) – 40% market share in 2022.
- Micron (USA) – 10% market share in 2022, aiming to grow to 20-25% by 2025.
Together, SK Hynix and Samsung are expected to maintain a combined 95% market share through 2024.
Why is the US Restricting HBM Exports to China?
The US announced new export restrictions on December 2, targeting HBM chips as part of a broader effort to curb China’s access to advanced technology with potential military applications.
This follows earlier measures by the Biden administration to limit China’s access to cutting-edge semiconductors. In response, Beijing imposed export controls on critical materials like germanium and gallium, essential for chipmaking.
Impact of Restrictions on China
China’s ability to produce HBM lags behind global leaders like SK Hynix, Samsung, and Micron. While domestic companies such as Yangtze Memory Technologies and Changxin Memory Technologies are ramping up production, experts believe the restrictions will delay China’s progress.
“In the short run, the US restrictions will block China’s access to high-quality HBM,” says Jeffrey Chiu, CEO of Ansforce. “However, in the long term, China is likely to produce HBM independently, albeit with less advanced technologies.”
Why is HBM So Important?
The rapid rise of generative AI, which powers tools like ChatGPT, has driven soaring demand for HBM. AI applications require vast amounts of data to train large language models, and HBM’s superior performance ensures smooth, glitch-free operations.
With HBM accounting for an increasing share of the memory chip market—projected to exceed 30% by 2025—it’s clear that these chips are indispensable for the future of technology.

The Bigger Picture
The US-China tech rivalry underscores the strategic importance of semiconductors like HBM. As AI continues to revolutionize industries, controlling access to critical technologies could shape the balance of power in the global tech landscape.
By restricting HBM exports, the US aims to maintain its technological edge while limiting China’s progress in AI development. However, with China’s determined push toward tech self-sufficiency, the competition is far from over.
This article was rewritten by JournosNews.com based on verified reporting from trusted sources. The content has been independently reviewed, fact-checked, and edited for accuracy, neutrality, tone, and global readability in accordance with Google News and AdSense standards.
All opinions, quotes, or statements from contributors, experts, or sourced organizations do not necessarily reflect the views of JournosNews.com. JournosNews.com maintains full editorial independence from any external funders, sponsors, or organizations.
Stay informed with JournosNews.com — your trusted source for verified global reporting and in-depth analysis. Follow us on Google News, BlueSky, and X for real-time updates.














